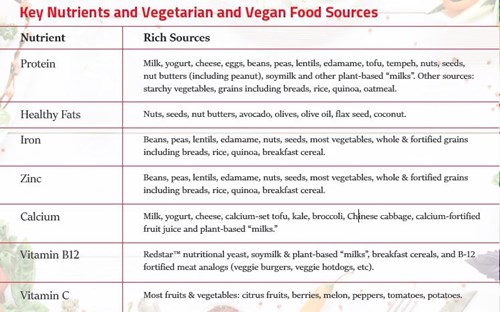
A balanced vegan diet has many benefits. You can choose from whole grains as well legumes and fortified food. Legumes are also rich in protein, and you can also get some iron and choline from nuts. Whole grains can also be a great source of fiber. A balanced vegan diet is also low in fat and cholesterol.
Whole grains are a staple food group
Whole grains are an important part of a vegan diet. They provide important nutrients and fiber. Whole grains can also be used as a base for baking and salads.
Legumes are rich in protein
Legumes are an excellent source of protein, and can be used as a replacement for red meat. They are high-fiber and low in saturated oil. Lentils are not only high in protein but also have high fiber levels, which helps with digestion and reduces the chance of developing heart disease.
Fortified foods contain iron
Fortified foods can be an excellent source of iron. But be aware that not all fortified foods are equal. There are two types iron. Heme iron is only found in animal products and nonheme iron is found in plant foods. Heme iron can be more easily absorbed by the human body. It is important to keep track of your iron intake if you are vegan.
Choline can be found in nuts
Choline can be found in many plant-based foods including nuts. This mineral is also present in grains and legumes. In fact, the National Institutes of Health describes some of these foods as "rich sources" of choline. Some vegetables and beans actually contain more choline that fish, meats, and dairy products. However, it is important to note that dairy products are high in saturated fat, which increases the risk of heart disease and Alzheimer's disease.
Zinc is lacking in vegan diets
Research suggests that vegans may need to consume more zinc to ensure a healthy body. The problem lies in the fact that vegans are usually not consuming enough zinc in their diets. There are many ways to get your daily zinc intake. You can eat more vegetables and fruits to meet your daily zinc requirements. Similarly, you can add a vegan zinc supplement to your diet.
Iron deficiency can affect baby's brain
Iron plays a critical role during brain development in the fetus. Iron is crucial for the hippocampus, which is the time when the brain is still in development. Iron deficiency during infancy affects various areas of the brain, depending on the degree and timing of deficiency. The brain needs iron for growth and developmental purposes, so it is crucial that an expectant mom provides the necessary iron.

Zinc deficiency can impair red blood cell production
Babies and older adults are at greatest risk for developing zinc deficiency. Mothers who are pregnant or breastfeeding require more zinc than usual. Zinc, which aids in the growth of the baby, is an essential nutrient for pregnant women. Zinc deficient people can have problems with their reproductive system. This includes impotence and hypogonadism (a lack of testosterone). Globally, there are 1.1 billion people who are deficient in zinc.
FAQ
How can I live the best life possible every day?
Find out what makes YOU happy. This is the first step in living a life that you love. You can then work backwards once you have identified your happiness. You can also ask others how they live their best lives everyday.
You can also check out books like "How to Live Your Best Life" from Dr. Wayne Dyer. He speaks about happiness and fulfillment in all areas of life.
What is the problem with BMI?
BMI is the acronym for Body Mass Index. It measures body fat based upon height and weight. This formula calculates BMI.
Weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared.
The result is expressed as a number from 0 to 25. Scores between 0 and 25 indicate obesity. Scores higher than 18.5 are considered overweight. Scores higher than 23 are considered obese.
A person who weighs 100 kg and has a height of 1.75 m will have a BMI of 22.
What is the difference of a virus from a bacteria?
A virus is an organism microscopic that can't reproduce outside its host cells. A bacterium can be described as a single-celled organism which reproduces by splitting in two. Viruses measure only 20 nanometers in diameter, but bacteria is up to 1 millimeter in size.
Viruses can spread from contact with bodily fluids that are infected such as saliva, urine or semen. Bacteria are often spread via direct contact with contaminated surfaces and objects.
Viral infections may enter the body through cuts, scrapes. bites and other skin breaks. They may also enter through the nose, mouth, eyes, ears, vagina, rectum , or anus.
Bacteria can enter the body through cuts, scrapes burns and other injuries to the skin. They may also enter our bodies from food, water, soil, dust, and animals.
Both bacteria and viruses can cause illness. But viruses can't multiply within their host. Viral infections can only cause diseases in living cells.
Bacteria can spread within the host and cause illness. They can even invade other parts of the body. Antibiotics are needed to eliminate them.
What is the difference between calories and kilocalories?
Calories are units that measure the energy content of food. Calories is the unit of measurement. One calorie is equal to one degree Celsius in energy.
Kilocalories are another way to describe calories. Kilocalories are measured in thousandths of a calorie. 1000 calories are equal to one kilocalorie.
Statistics
- In both adults and children, the intake of free sugars should be reduced to less than 10% of total energy intake. (who.int)
- According to the 2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans, a balanced diet high in fruits and vegetables, lean protein, low-fat dairy and whole grains is needed for optimal energy. (mayoclinichealthsystem.org)
- The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend keeping added sugar intake below 10% of your daily calorie intake, while the World Health Organization recommends slashing added sugars to 5% or less of your daily calories for optimal health (59Trusted (healthline.com)
- Extra virgin olive oil may benefit heart health, as people who consume it have a lower risk for dying from heart attacks and strokes according to some evidence (57Trusted Source (healthline.com)
External Links
How To
What does the meaning of "vitamin?"
Vitamins are organic substances found naturally in food. Vitamins allow us to absorb nutrients from food. Vitamins cannot be produced by the body. They must be obtained from food.
Two types of vitamins exist: water soluble and oil soluble. Water-soluble vitamins dissolve easily when they are dissolved in water. These include vitamin C (thiamine), Vitamin B1 (riboflavin), Vitamin B2 (riboflavin), Vitamin B3 (niacin), Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), Vitamin C, B1 (thiamine), Vitamin B2 (riboflavin), Vitamin B3 (niacin), and Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine). Fat soluble vitamins are stored in the liver and fatty tissue. Vitamin D, E, K and A are some examples.
Vitamins can be classified by their biological activity. There are eight main types of vitamins:
-
A - Essential for healthy growth and health maintenance.
-
C - important for proper nerve function and energy production.
-
D - essential for healthy teeth and bones.
-
E - needed for good vision and reproduction.
-
K - Essential for healthy muscles and nerves.
-
P - Vital for strong bones and teeth.
-
Q – aids digestion and absorption.
-
R - necessary for making red blood cells.
The recommended daily intake (RDA), of vitamins varies with age, gender and physical conditions. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has established the RDA values.
For adults 19 years and over, the RDA vitamin A intake is 400mg/day. For fetal development, pregnant women require 600 micrograms per daily. Children ages 1-8 require 900 micrograms per day. Children under 1 year old require 700 micrograms daily, while infants over one year old need 500 micrograms every day. This decreases between 9 and 12 months.
Children aged 1-18 require 800 micrograms of sugar per day, while those who weigh more than 1200 need 1000. For their nutritional needs, underweight children need 1200 mg per day.
Children aged 4-8 years old who have been diagnosed as having anemia require 2200 micrograms of vitamin C per day.
2000 micrograms daily is required for adults over 50 to maintain their general health. Mothers who are pregnant, nursing, or have a high nutrient need will require 3000 micrograms a day.
1500 micrograms is the recommended daily intake for adults aged 70+, as they lose 10% of their muscle every ten years.
Women who have been pregnant or are lactating require more than the RDA. Pregnant woman need 4000 micrograms daily in pregnancy and 2500 per day after childbirth. Breastfeeding mothers require 5000 micrograms daily when breast milk production is occurring.